3D Printing | Additive Manufacturing
From protyping to on-demand production.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, is a family of processes that produces objects by adding material in layers that correspond to successive cross-sections of a 3D model. Plastics and metal alloys are the most commonly used materials for 3D printing, but it can work on nearly anything—from concrete to living tissue. Unlike subtractive manufacturing which creates its final product by cutting away from a block of material, additive manufacturing adds parts to form its final product.
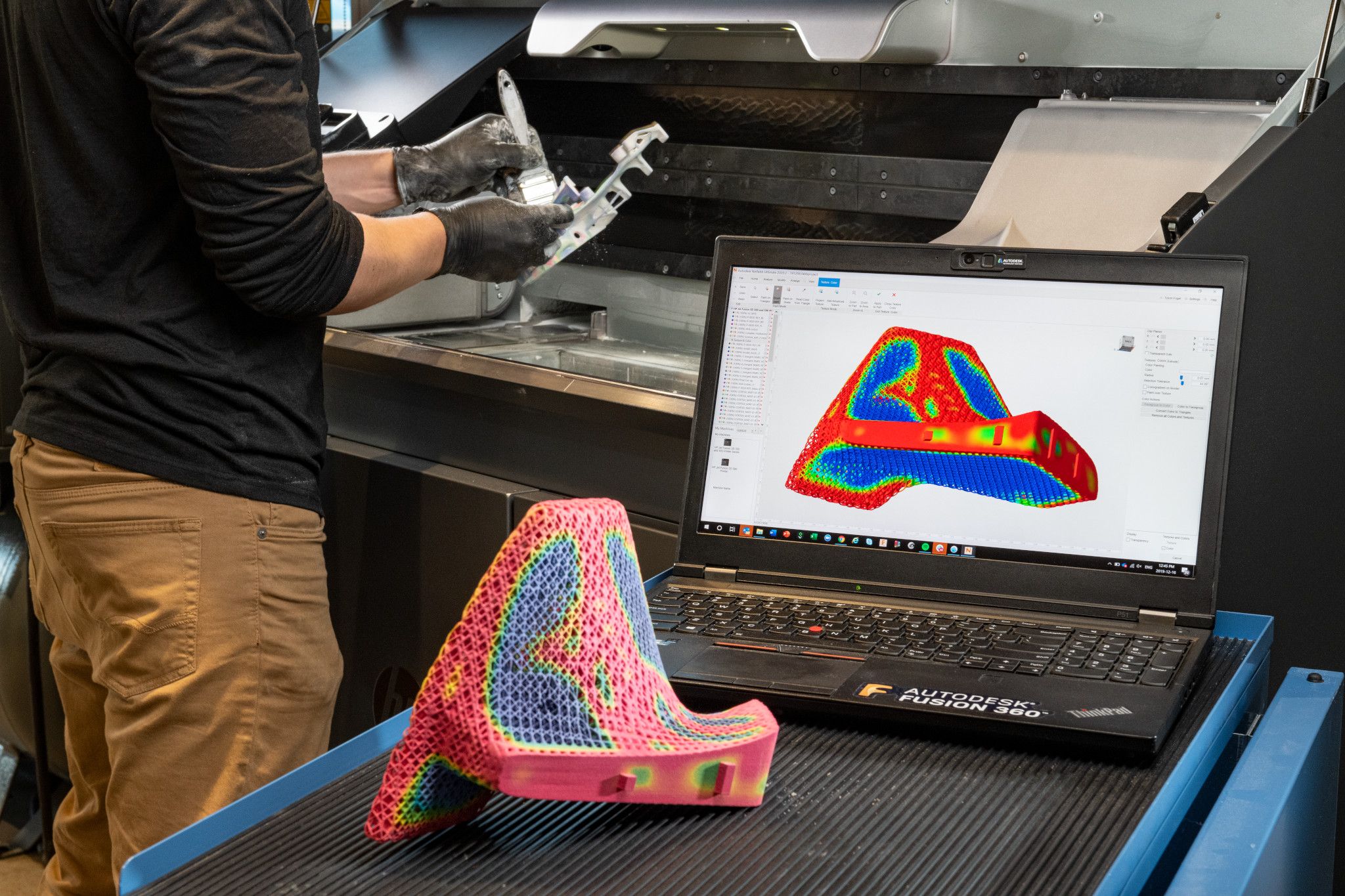
What is 3D printing used for?
Efficiently make one-off parts and create highly complex geometries that are only possible with 3D printing.
PROTOTYPING
3D printing has long been used to quickly create prototypes for visual aids, assembly mockups, and presentation models.
LIGHTWEIGHT PARTS
Fuel efficiency and emissions reductions are driving the need for lightweight parts via 3D printing in aerospace and automotive applications.
FUNCTIONALLY ENHANCED PRODUCTS
3D printing removes many of the constraints imposed by traditional manufacturing processes that prevent engineers from truly designing for optimal performance.
CUSTOM MEDICAL IMPLANTS
To achieve osseointegration, manufacturers are using 3D printing to precisely control surface porosity to better mimic real bone structure.
TOOLINGS, JIGS, AND FEATURES
METAL CASTING PATTERNS
Types of additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing can encompass multiple processes, depending on the hardware, material requirements, and product application.
 VAT PHOTOPOLYMERIZATION
VAT PHOTOPOLYMERIZATION
A vat of photopolymer liquid is cured by focused UV light that builds parts layer by layer for a high-detail surface finish.

BINDER JETTING
A powder substrate is hardened when the printing head deposits a drop of binding fluid in a layering process. Includes full-color prototype fabrication.
 MATERIAL JETTING
MATERIAL JETTING
Used where surface finish and form testing are needed; a printhead lays down successively solidifying layers of UV curable material to form prototyped designs.
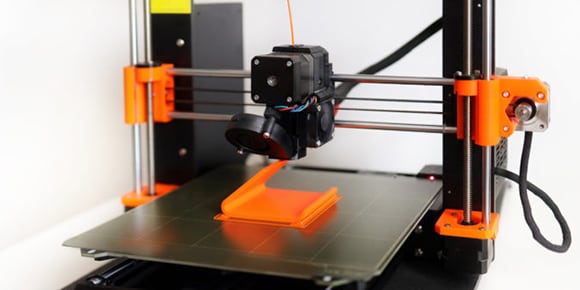
MATERIAL EXTRUSION
Fused deposition modeling is a common 3D printing process in which a heated nozzle extrudes a plasticized material to form products from a sliced CAD model.
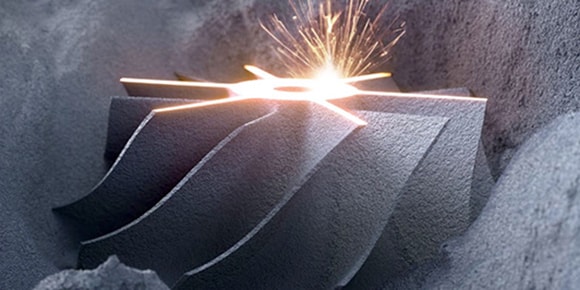
POWDER BED FUSION
Laser or electron beams rapidly fuse layered powder material, such as various metals, together. This technique is used for circuits, structures, and parts.

SHEET LAMINATION
Ribbons of metal or paper are bonded through ultrasonic welding or adhesive, respectively; the finished shaping is completed through further material removal processes.

DIRECTED ENERGY DEPOSITION
Repairs or adds to existing components by using a multi-axis nozzle to extrude laser-melted material, commonly metal powders, onto the printing surface.

METAL CASTING
Using generative design and simulation software to produce complex metal parts helps manufacturers get more value from proven metal casting processes.



