What is Autodesk CFD?
Autodesk CFD software provides fast, accurate, and flexible fluid flow and thermal simulation tools to help you make better design decisions earlier in the product development process. Autodesk CFD enables you to make great products by easily exploring and comparing design alternatives using an innovative Design Study Environment and automation tools.
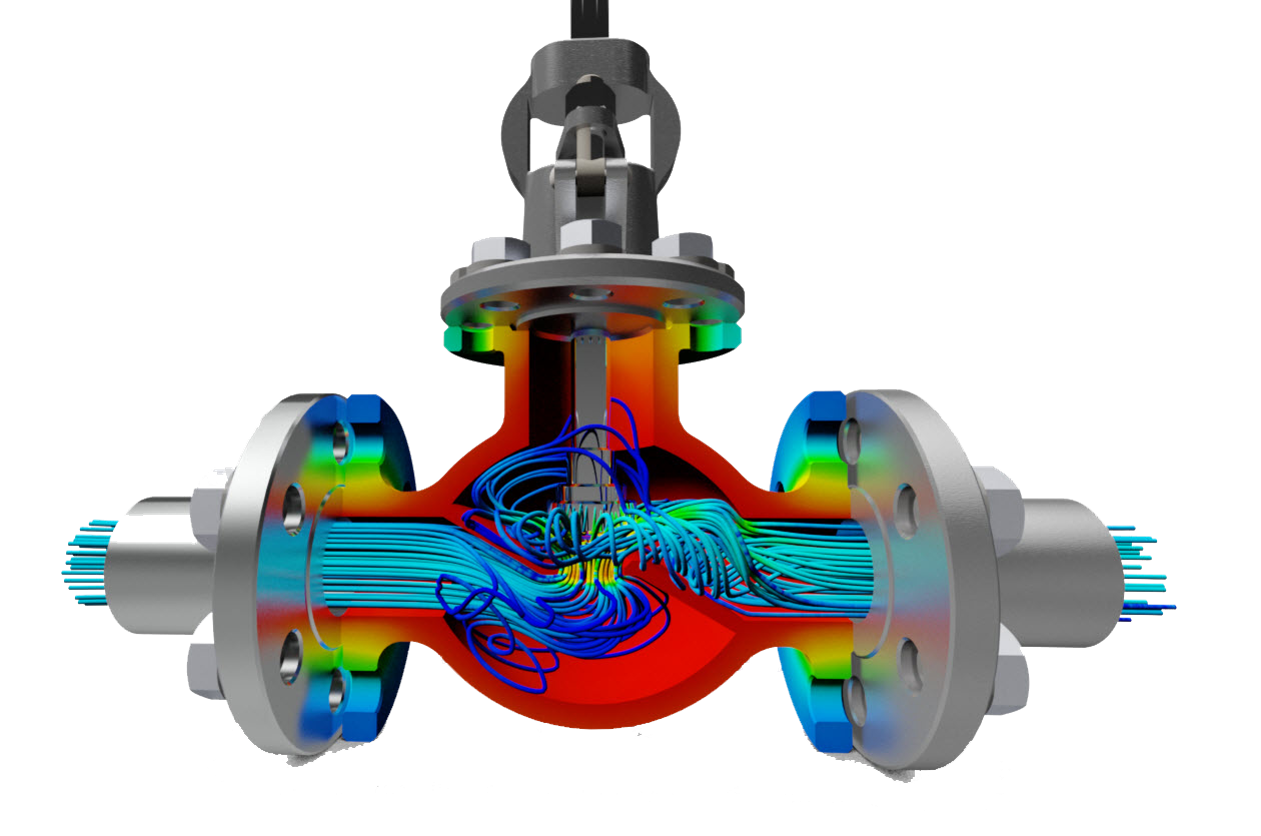
Industrial Flow Control
CFD can help manufacturers of flow control devices like valves, regulators, turbines, and compressors, to simulate the fluid flow through a 3D CAD model. The intuitive interface works directly with your Autodesk Inventor or other 3D CAD models.
- Visualize flow fields and model complex cavitation, free surface, and erosion as well as key performance characteristics such as velocity profiles and pressure drop.
- Reduce pressure drop or optimize flow distribution with the ability to simulate advanced capabilities such as fluid and solid interaction. This allows the designer to take into account moving solids like centrifugal pumps, turbo-machinery, and moving valves. Users can leverage CFD upfront during design development to experiment and innovate, and downstream for failure analysis.
- Simulate flow startup, capture transient pressure fluid flow development, and simulate the mixing of two similar fluids by using a scalar mixing condition.
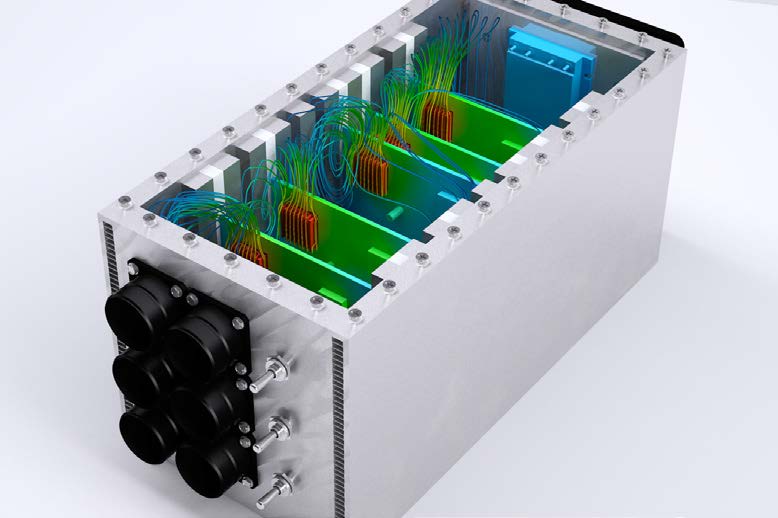
Electronics Cooling
Use CFD to test the thermal performance of your electronics design and face challenges such as optimizing cooling, determining optimum locations of heat sinks and heat pipes, thermal management, and study of transient effects. Electronics specific functionality includes:
- Idealizations which include simplified heat sink model, PCB characterizer, compact thermal models (CTM), thermoelectric cooler devices (Peltier modules), and thermostat-controlled fans.
- CFD handles all the modes of heat transfer including: conduction, convection (forced and natural), and radiation.
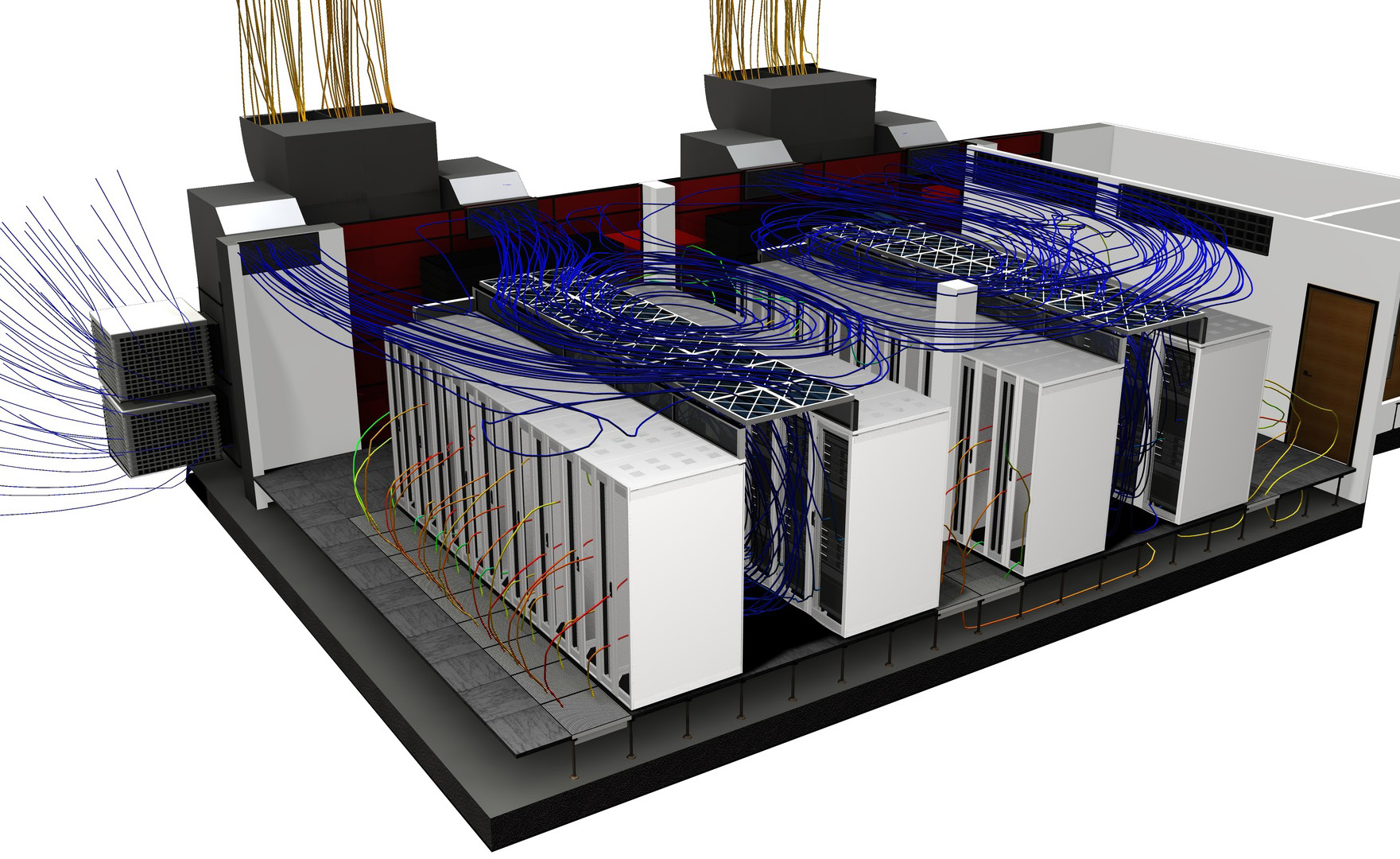
Architectural and MEP
Architects and mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) professionals can take advantage of CFD to understand airflow and thermal behavior in the built environment.
- Better predict contaminant dispersion and smoke migration in and around buildings as well as study the long-term effects of diurnal heating.
- Includes a range of CFD modeling and thermal modeling tools that are of particular interest to architectural and MEP professionals.
- Model radiant heat transfer, humidity and solar effects on occupant comfort.
- Use Local Mean Age results to best determine optimum placements of registers and returns.
- Predict contaminant dispersion and smoke migration both inside and outside buildings; increase building efficiency by understanding and optimizing design features.
Why CFD?
Improve energy efficiency
Make critical design decisions that reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency.
Reduce failure risk
Solve potential failures during the design process to extend operational life of products and systems.
Minimize physical prototyping costs
Create digital prototypes with simulations to help reduce costly physical models.

